Serevent is a synthetic drug related in chemical structure to phenyl-substituted β-amino alcohols, for administration by inhalation. Salmeterol refers to selective beta2-adrenoreceptor agonists group with long-lasting bronchodilatory action. According to its chemical composition, as well as other beta2-agonists, it is a racemate of two enantiomers (S-salmeterol and R-salmeterol). Salmeterol was created in 80s years of the twentieth century in GlaxoSmithKline laboratory, UK, and is used in clinical practice since 90s years of the twentieth century.
Pharmacological Properties
Drug mechanism of action is stimulation of beta2-adrenoceptors in bronchial smooth muscle through intracellular activation of adenylate cyclase, which forms a complex with G-protein, under the influence of which cAMP formation and of protein kinase A stimulation increases, leading to internal organs smooth muscle relaxation. Serevent is a noncompetitive beta2-adrenoceptor antagonist, which provides drug high selectivity and long-lasting action (until 12:00 after inhalation). Serevent is not a complete beta2-adrenoceptor agonist, which leads to small delay in drug action onset, but to fewer side effects. Its inhalation affects only beta2- adrenoceptors in bronchi and does not affect receptors in other organs. Serevent only slightly affects myocardial beta1-adrenoceptors.
At long-term use, drug tolerance development is observed, and significantly exceeding average therapeutic dosage greatly increases serious adverse effects probability, including those associated with myocardial adrenoreceptors activation (including tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, myocardial ischemia, orthostatic hypotension, QT interval prolongation), and possibility of «ricochet» effect occurrence (although lower than with other adrenoceptor agonists) – increased bronchospasm at excess average therapeutic dosage or too frequent drug use. For increasing the effect it is recommended to use it together with inhaled corticosteroids. Serevent is not indicated for acute asthma attacks relief due to the relatively slow onset of action.
Pharmacokinetics
Serevent is rapidly absorbed in respiratory tract after administration by inhalation, the onset of action is observed within 10 – 20 minutes after drug inhalation and lasts until 12 hours. It does not create high concentrations of blood and internal organs, according to research, the drug passes through the placental barrier and is excreted in breast milk. The drug is metabolized in the liver to inactive metabolites. It is excreted primarily with feces, partly with urine. Half-life period is 5,5 hours, complete drug clearance is observed within 72 hours.
Indications
Serevent is used at bronchial asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases by inhalation for long-term airway obstruction treatment, including night asthma attacks, and asthma attacks after exercise prevention.
Dosage
Inhalation.
- For asthma attacks prevention, including at night, usual dosage for adults and children over 12 years – 2 inhalations (50 mcg) twice a day (morning and evening).
- For bronchospasm provoked by exercise prevention – 2 inhalations at least 30 – 60 minutes before exercise.
- For severe asthma treatment – 100 mcg 2 times a day.
Precautions: not applicable for bronchospasm relief. With caution prescribed to patients with thyrotoxicosis, severe asthma, hypoxia of any origin.
The therapeutic effect may be reduced when an inhaler is cooled.
If recommended dosage is not effective, you need to increase it. It should be understood that regular use, at most patients, need for additional short-lasting sympathomimetics use reduces.
Do not allow contact with eyes.
Side Effect
When using this bronchial asthma drug frequency of side effects is small. Overall side effects incidence when using the drug is 16%; common side effects (headaches, seizures, tremors, tachycardia) are observed with a frequency of 1,5 – 3% with 50 mcg and 7 – 8 % with 100 mcg. Other side effects occur rarely:
- allergic reactions (skin rash, itching, urticaria fever, Quincke’s edema);
- sickness;
- vomiting;
- stomatitis and pharyngitis due to mucous membranes irritation;
- arrhythmia (including atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia and extrasystoles);
- arthralgia;
- anxiety;
- paradoxical bronchospasm;
- hypokalemia.
Contraindications
Serevent is contraindicated in case of hypersensitivity to its components. The drug should be used with caution in case of:
- pregnancy;
- lactation period;
- hyperthyroidism.
Salmeterol is used at children older than 4 years.
Pharmaceutical Form
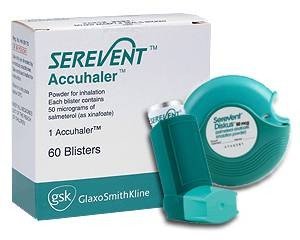 Serevent is available as aerosol in dosage of 25 mcg/dose containing 60 and 120 doses, and in powder for inhalation in discus in 50 mcg/dose containing 4 doses. It is also available in combination with fluticasone in the form of aerosol or powder for inhalation in discus.
Serevent is available as aerosol in dosage of 25 mcg/dose containing 60 and 120 doses, and in powder for inhalation in discus in 50 mcg/dose containing 4 doses. It is also available in combination with fluticasone in the form of aerosol or powder for inhalation in discus.
Prohibition for Use in Sports
Serevent is prohibited for use to athletes during competitions by World Anti-Doping Agency (https://www.wada-ama.org/). But some athletes with asthma have permission for drug use.
Posted by Dr. Himanshu Singh

 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch Français
Français Italiano
Italiano Español
Español Svenska
Svenska Português
Português 日本人
日本人 Dansk
Dansk Norsk
Norsk Suomi
Suomi Czech
Czech